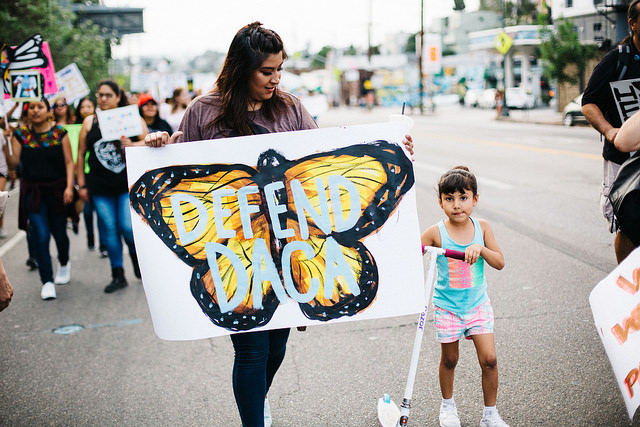
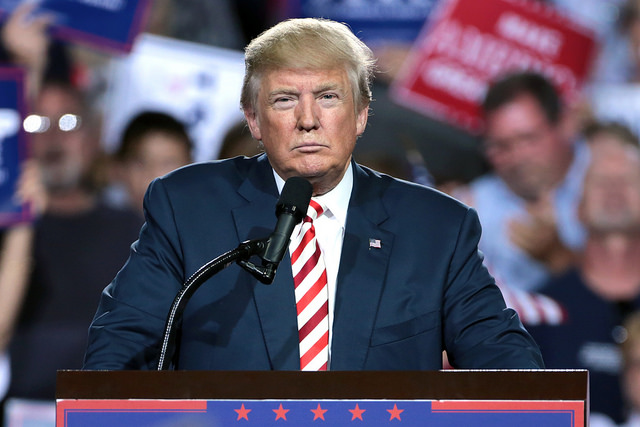
As of today, lawmakers in Congress have 115 days to pass legislation allowing more than 800,000 undocumented immigrants, known as Dreamers, who were brought to the United States as children, the opportunity to remain in the United States lawfully.
If Congress does not act by the March 5th deadline terminating the DACA program, it is likely that the President will give Congress more time to pass such legislation. The President has reiterated that he wants the solution to come from Congress, and will not act unilaterally to shield Dreamers from deportation.
Attorney General Jeff Sessions has signaled to Congress that the future of DACA remains in their hands, recognizing that they have an “opportunity to do something historic.” Republican politicians have thus far shown their willingness to work with Democrats to pass legislation that would grant Dreamers not only protection from deportation and the ability to reside in the United States lawfully, but an opportunity to obtain citizenship. Notoriously conservative Republican Senator, Roy Blunt, along with others has said that he would be willing to support legislation granting Dreamers a path to citizenship, and said as early as Tuesday that deporting Dreamers to a country they did not grow up in would be “totally unreasonable.”
President Trump of course has said that he does not support legislation that would give Dreamers a path to citizenship, however a majority of Congress could override a Presidential veto should such a piece of legislation come to pass. Legislation to protect Dreamers from deportation would however come with certain conditions. The President, as well as Republicans, are pushing for provisions that would secure funding for the wall to be constructed along the U.S./Mexico border and enhance border security. Republican Congressman Dan Newhouse has said that the consensus among Congress is that “it is the responsibility of Congress, and not the administration to make immigration law.”
 Visa Lawyer Blog
Visa Lawyer Blog