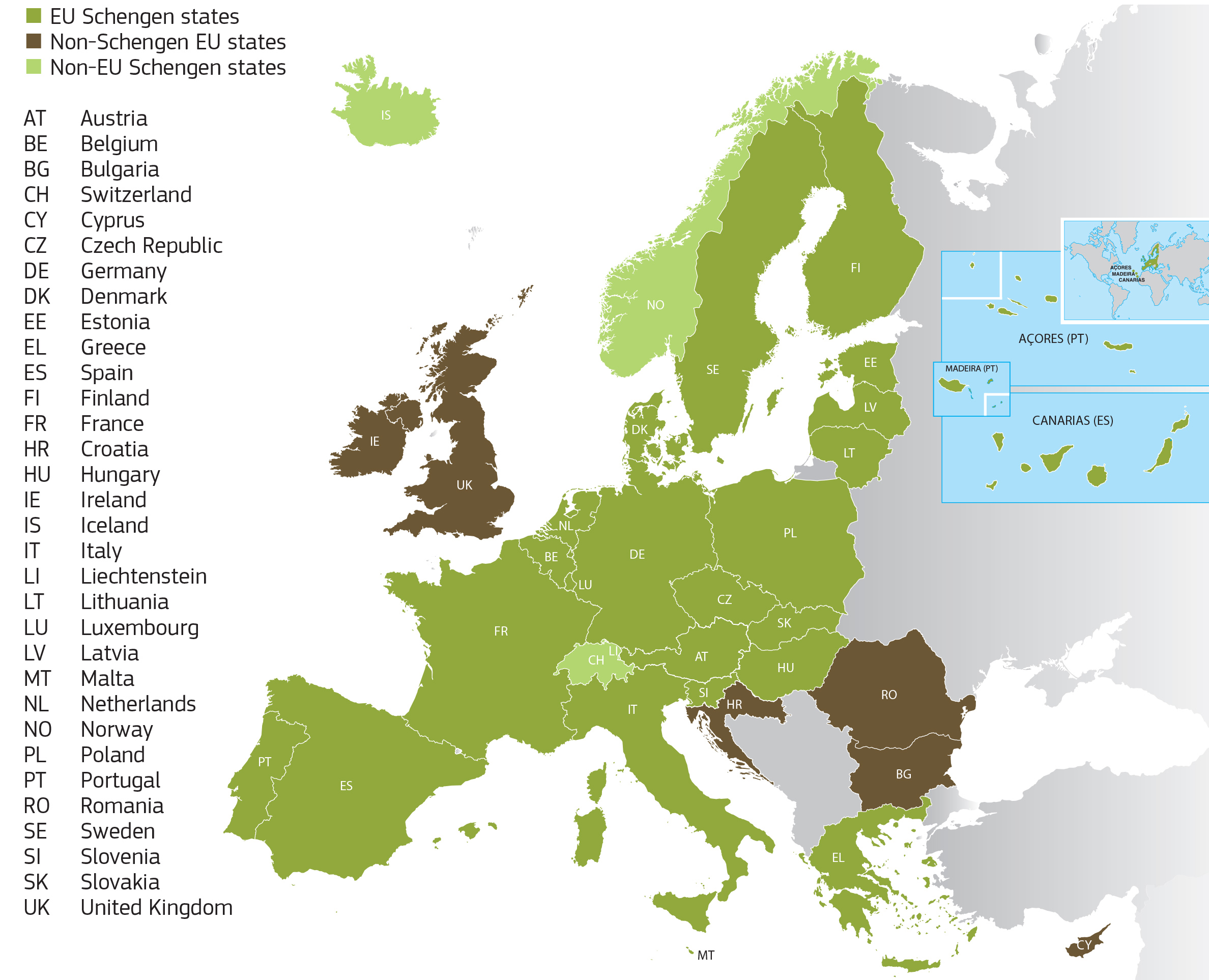
In light of the global Coronavirus pandemic, on March 11, 2020, the President signed a presidential proclamation suspending and limiting the entry of immigrants and nonimmigrants who were physically present within the Schengen Area (most EU states) during the 14-day period preceding their entry or attempted entry into the United States, effective 11:59 eastern time Friday, March 13, 2020.
The proclamation will remain in effect until terminated by the President at his discretion based on recommendations by the Secretary of Health and Human Services.
The proclamation does not apply to persons aboard a flight scheduled to arrive in the United States that departed prior to 11:59 eastern time on March 13, 2020.
Who is exempted from the Proclamation?
The proclamation will not apply to the following categories of people:
- lawful permanent resident of the United States;
- any alien who is the spouse of a U.S. citizen or lawful permanent resident;
- any alien who is the parent or legal guardian of a U.S. citizen or lawful permanent resident, provided that the U.S. citizen or lawful permanent resident is unmarried and under the age of 21;
- any alien who is the sibling of a U.S. citizen or lawful permanent resident, provided that both are unmarried and under the age of 21;
- any alien who is the child, foster child, or ward of a U.S. citizen or lawful permanent resident, or who is a prospective adoptee seeking to enter the United States pursuant to the IR-4 or IH-4 visa classifications;
- any alien traveling at the invitation of the United States Government for a purpose related to containment or mitigation of the virus;
- any alien traveling as a nonimmigrant pursuant to a C-1, D, or C-1/D nonimmigrant visa as a crewmember or any alien otherwise traveling to the United States as air or sea crew;
 Visa Lawyer Blog
Visa Lawyer Blog