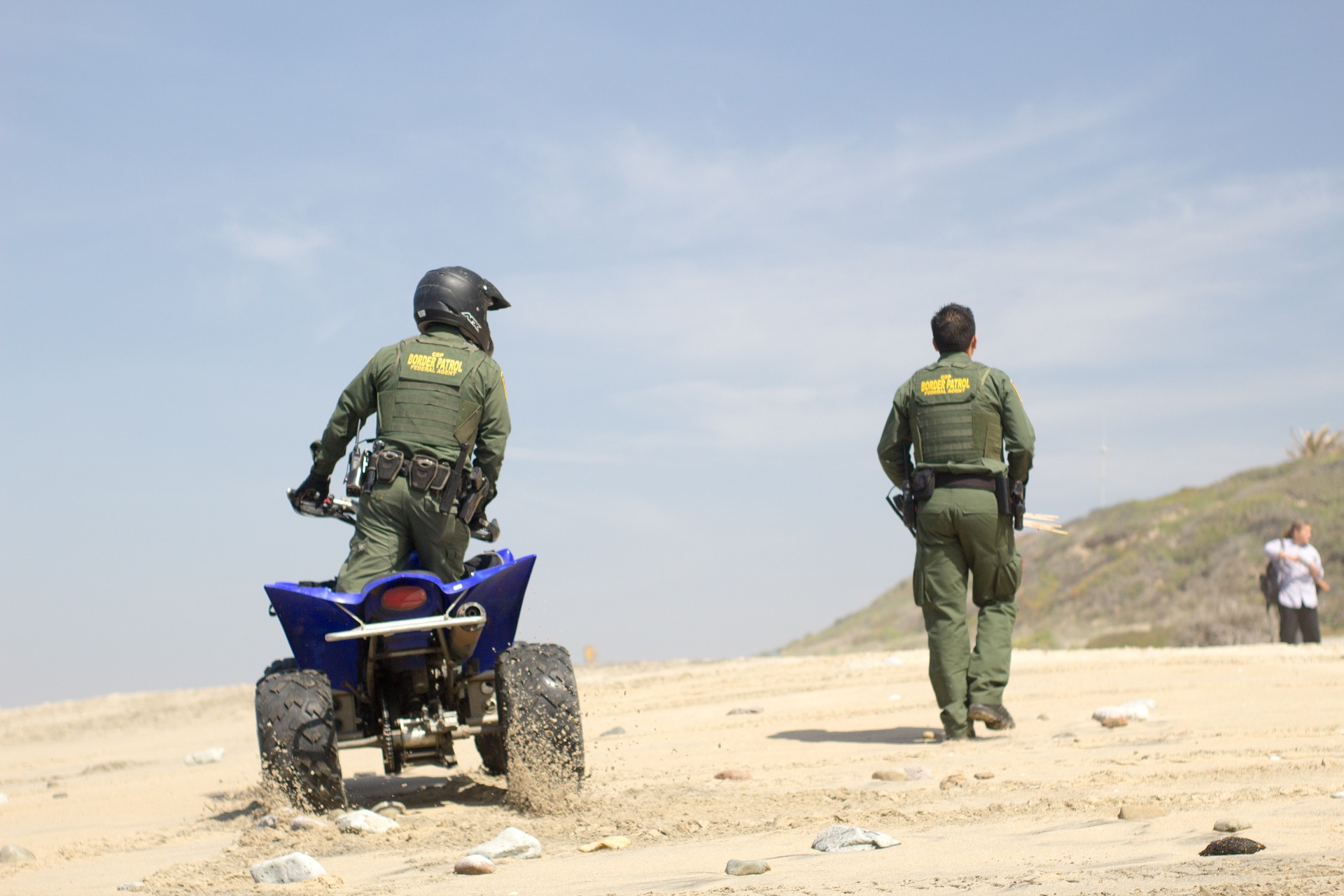
The Trump administration is in full gear to expedite the removal of hundreds of asylum seekers, most of which are arriving from Central America.
As early as October of 2019, the Washington Post made public the existence of a confidential pilot program coordinated by the Department of Homeland Security and Department of Justice designed to swiftly deport asylum-seekers within a matter of days.
Under the program, Prompt Asylum Claim Review, the government would take a maximum period of 10 days to consider applications for asylum from individuals arriving at the U.S./Mexico border. Those denied would be swiftly removed from the country and returned to their homeland.
As a result, asylum determinations that usually take years to be made, will now be made in a matter of days.
It is easy to see how this type of accelerated removal from the country raises serious due process concerns and delegitimizes the complex asylum process.
A recent lawsuit filed by the American Civil Liberties Union against the Department of Homeland Security reveals that asylum seekers placed in this program are given only one window of approximately 30 minutes to one hour to call family members or retain counsel, and even where detainees have successfully retained counsel, CBP has denied attorneys physical access to speak to detainees, prohibited in-person meetings, and telephonic access. Where attorneys have tried to reach clients before their credible fear interviews, or hearings before an immigration judge, CBP has forced a detainee to proceed without opportunity to counsel with their attorney.
 Visa Lawyer Blog
Visa Lawyer Blog