We kick off the start of a brand-new week with some important new updates regarding the new COVID-19 vaccination requirement for all immigrant visa applicants, fiancé(e) visa applicants, and nonimmigrant visa applicants. We also share with you some new information regarding Croatia’s designation as a country participating in the Visa Waiver Program. When can Croatians start to apply for ESTA? Find out here!
COVID-19 Vaccine Requirements for Immigrant Visa Applicants Overseas
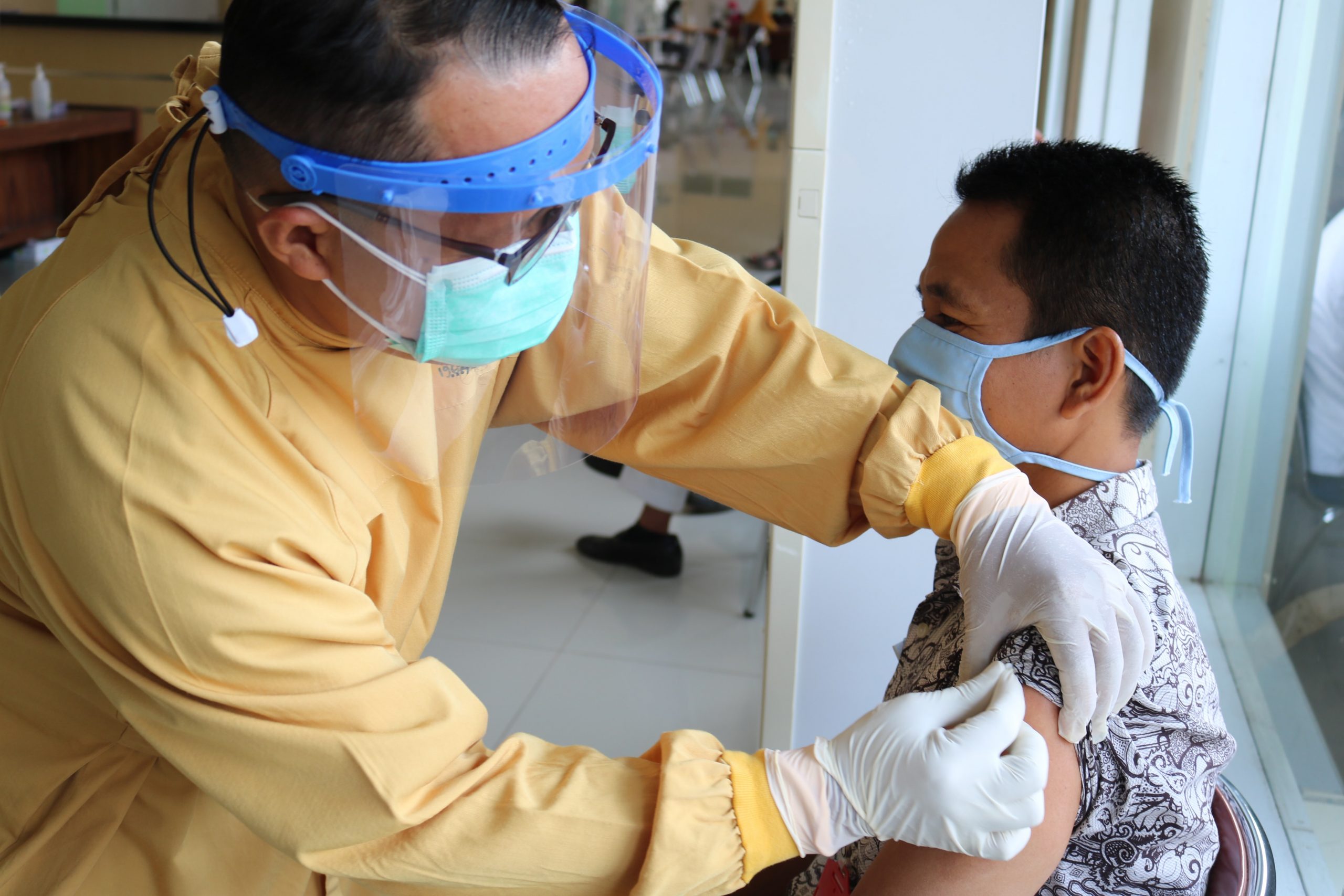
The Department of State has issued a brand-new press release informing the public that effective October 1, 2021, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Technical Instructions for panel physicians, will now require all immigrant visa applicants, all K fiancé(e) visa applicants, and nonimmigrant visa applicants who are referred to the panel physicians to receive a full COVID-19 vaccine series (1 or 2 doses depending on formulation) as part of their medical exam prior to being issued a visa. The CDC is requiring the COVID-19 vaccine to be approved through either the World Health Organization (WHO) or the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Blanket waivers for the COVID vaccination will be applied in countries where the vaccine is not routinely available or when the vaccine is not age appropriate. The Department of State is encouraging all immigrant visa applicants and others subject to a medical exam to get vaccinated against COVID-19 as soon as possible to avoid delays in their visa processing. If any of the below mentioned circumstances apply a blanket waiver may be available to you.
Circumstances in which Blanket Waivers are available for COVID-19 vaccinations:
- Where it is not age-appropriate to receive the vaccination
For COVID-19 vaccines, the age for which a particular vaccine can be administered differs by formulation. If the applicant is younger than the lowest age limit for the formulations in use (less than 12 years of age at the time of posting), this blanket waiver should be documented. - In cases where a contraindication exists – a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient.
If an applicant has a contraindication or precaution to the COVID-19 vaccine formulation available, the “Contraindicated” reason should be documented, and the vaccine should not be administered. If the applicant has had a severe reaction to the first dose that is considered a contraindication to receiving a second dose, the first dose should be documented in addition to the blanket waiver. Please refer to Interim Clinical Considerations for Use of COVID-19 Vaccines Currently Authorized in the United States for COVID-19 specific information about contraindications and precautions.
- Where a vaccine is not routinely available
If no COVID-19 vaccine is routinely available in the state where the Civil Surgeon practices, the “Not routinely available” reason should be documented. If vaccine is available to the applicant but due to limited supply, it would cause significant delay for the applicant to receive their vaccination, then this situation would also be considered “Not routinely available.”
 Visa Lawyer Blog
Visa Lawyer Blog